
What is Red Light Therapy?
Key Takeaways
- Simple & Safe: Red light therapy uses visible red (≈630–660 nm) and near-infrared light (≈810–850 nm) to energize cells, reduce inflammation, and promote healing.
- Science-Backed: Thousands of studies show benefits for pain, recovery, skin health, circulation, and even brain function.
- FDA-Cleared Uses: Approved for acne, arthritis, hair loss, circulation, and muscle/joint pain relief.
- How It Works: Light photons stimulate mitochondria (your cells’ “batteries”), improving energy production and restoring balance.
- Dose Matters: Results depend on wavelength, intensity (irradiance), and time. Too little = no effect; too much = diminishing returns.
- Dual Power: Red light works best at the surface (skin, healing, inflammation) while near-infrared penetrates deeper (muscles, joints, nerves, brain).
- Accessible at Home: Once only in clinics, high-quality panels (High EMF emitting) and wearables now make it practical for everyday use.
- Whole-Body Potential: Whether for performance, recovery, beauty, or chronic conditions, red light therapy offers a safe, drug-free way to support wellness.
What is Red Light Therapy?

Red light therapy is a treatment that uses specific ranges of visible red and invisible near-infrared light to deliver energy directly into your cells. By supporting how cells function, this light helps improve overall biological performance and recovery.
It’s often referred to by different names, such as:
- Low-level laser therapy (LLLT)
- Low-intensity light therapy (LILT)
- Photobiomodulation (PBM)
- Phototherapy
- Biostimulation
- Photonic stimulation
All of these terms describe the same process: using light to activate and restore cellular health.
Is Red Light Therapy Safe and Effective?
Red light therapy is FDA-cleared for several conditions, including acne, arthritis, poor circulation, muscle and joint pain, and even hair loss.
Beyond these uses, Red Light Therpay is backed by thousands of scientific and clinical studies. At the bottom of this page, you’ll find a list of conditions that Red Light Therapy has been shown to support.
Understanding Light Therapy: The Three Key Variables
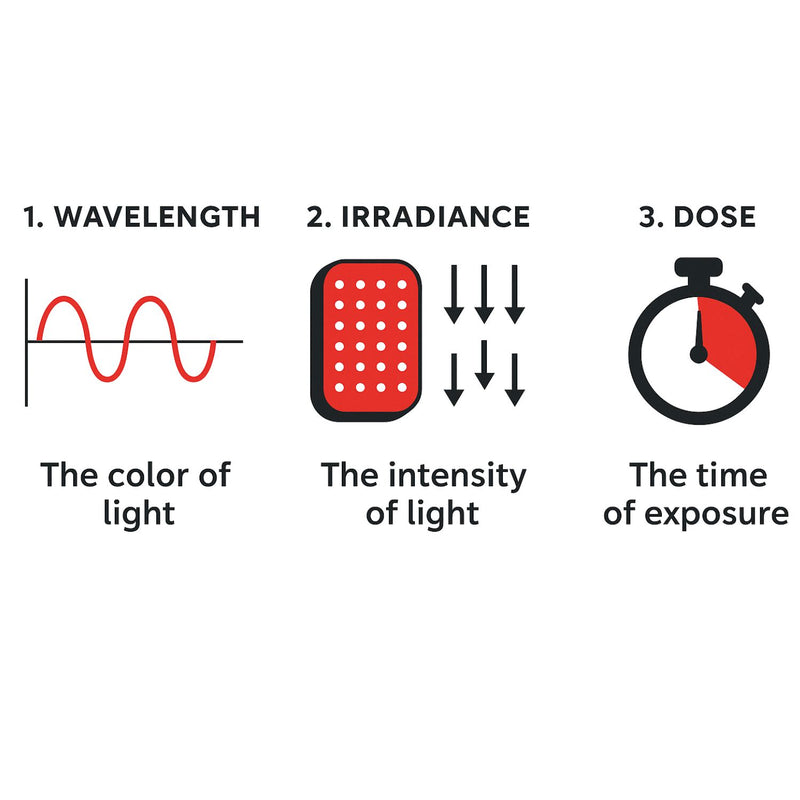
Before diving into red and near-infrared light therapy, it’s important to understand three key variables that determine how effective any treatment will be: wavelength, irradiance (power density), and dose (energy delivered).
By grasping these factors, individuals can better understand how red light therapy works, evaluate device specifications, determine optimal treatment times, and interpret clinical studies—making the benefits of both red and near-infrared light much clearer.
What is a Wavelength?
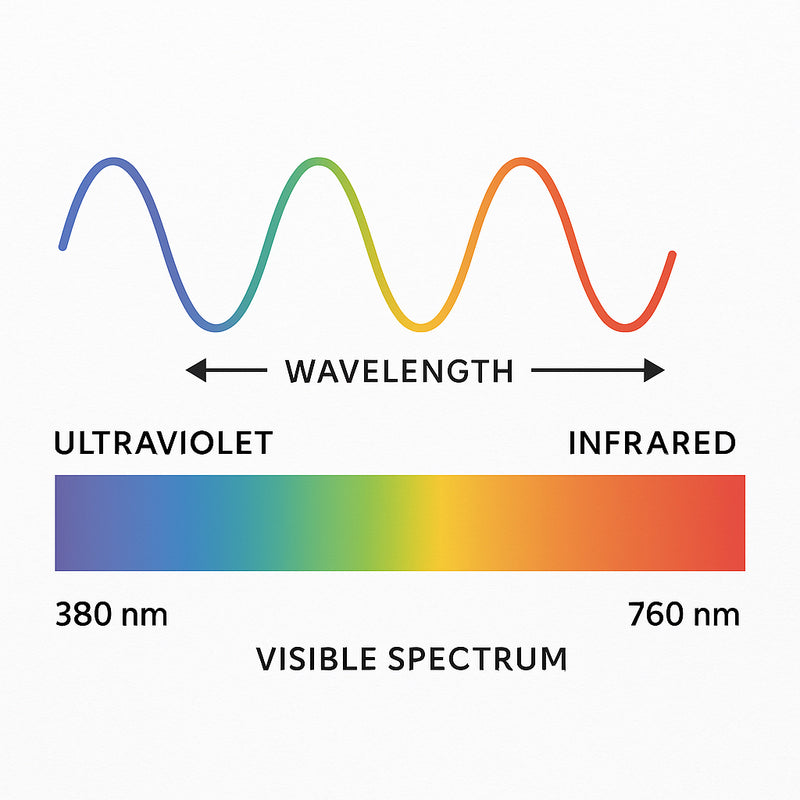
Red light therapy (RLT) is a treatment that uses low-level wavelengths of red and near-infrared light to stimulate natural healing processes in the body. Unlike ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun, which can damage skin, red and near-infrared light are safe and beneficial. They penetrate the skin without causing harm, targeting your cells at the mitochondrial level—the “powerhouse” of the cell.
The treatment is often delivered through LED panels, handheld devices, or wearable systems that emit light in the red (around 600–700 nanometers) and near-infrared (700–1,100 nanometers) spectrum.
What Is Irradiance?
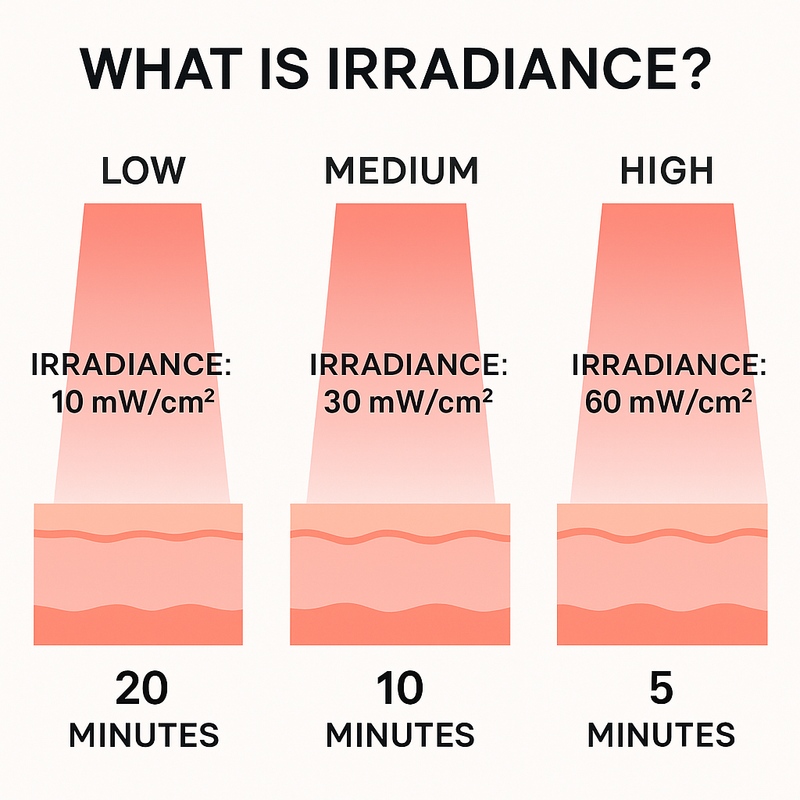
Irradiance is the power of light delivered to a surface, measured in milliwatts per square centimeter (mW/cm²).
- Think of it as the strength of the light beam hitting your skin.
- Higher irradiance = more energy delivered to cells (up to a therapeutic limit).
Why It Matters
- Too Low: Not enough photons → little to no effect.
- Too High: Oversaturation → diminishing or inhibitory effects.
- Just Right: The “sweet spot” where mitochondria are energized effectively.
Typical Ranges
- Low-Level Devices: 5–20 mW/cm² (longer sessions needed)
- Mid-Level Devices: 20–50 mW/cm² (common for consumer panels/wearables)
- High-Intensity Devices: 50–100+ mW/cm² (clinical-grade, shorter sessions)
The Balance of Dose
- Formula: Dose (J/cm²) = Irradiance (mW/cm²) × Time (seconds) ÷ 1000
Example: A device with 50 mW/cm² used for 600 seconds (10 minutes) delivers 30 J/cm².
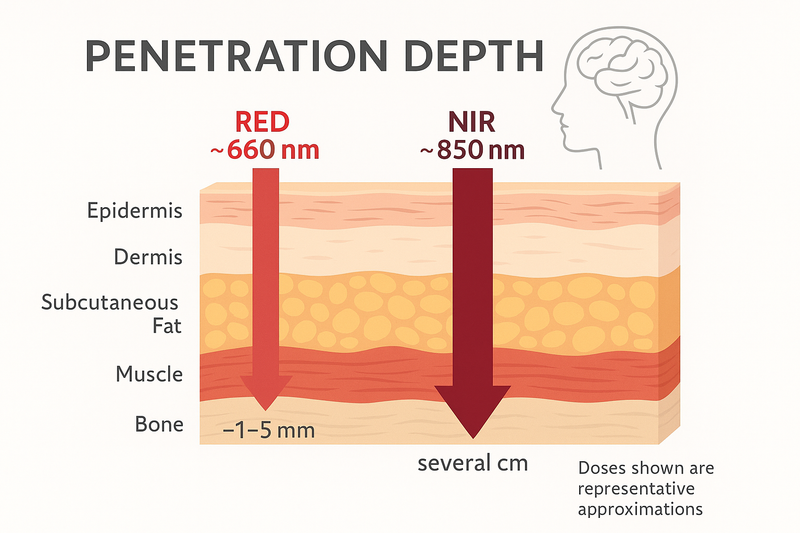
What Is Red Light?
- Range: 630–700 nanometers (nm)
- How it works: Unlike ultraviolet, blue, or green light that remain at the surface, red light penetrates deeper into skin and superficial tissues. Around 660 nm, it reaches cells in the upper dermis.
- Benefits: Supports skin health, stimulates collagen, reduces inflammation, and accelerates wound healing.
What Is Near-Infrared Light?
Near-infrared light spans from 700–1000 nm, with therapy devices often using about 850 nm.
While invisible to the eye, it’s felt as a gentle warmth, like sunlight on your skin or the glow of a campfire. NIR penetrates much deeper than red light—several centimeters into the body—reaching muscles, joints, nerves, and even the brain.
It helps improve circulation, increase cellular energy, and support deeper recovery and repair.
👉 Note: The human eye can only detect light up to ~700 nm. NIR lies just beyond that.
Red vs. Near-Infrared Light Comparison: Depth & Effects
What are the 3 Primary Benefits of Red Light Therapy?
- Improves Circulation – Promotes blood vessel dilation and supports healthy blood flow.
- Boosts Cellular Energy – Stimulates mitochondria to produce more ATP, fueling your cells’ natural repair processes.
- Reduces Inflammation – Helps lower inflammatory signals and supports faster recovery.
1. Increased Blood Circulation
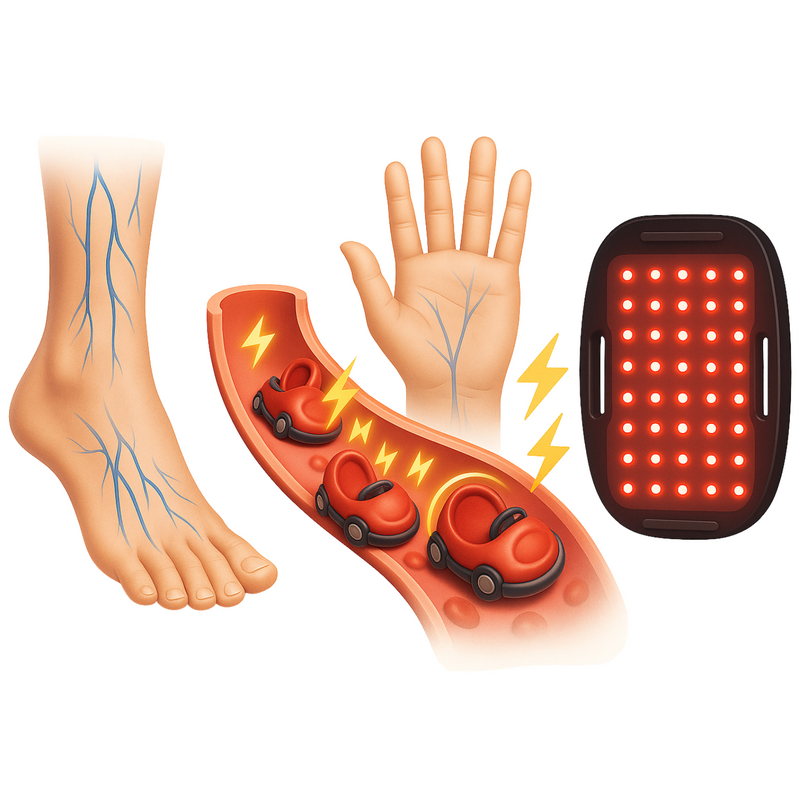
On a cellular level, “sticky” blood is often the result of a disruption in the electrical charge of cell membranes. Healthy blood cells carry a proper negative charge on their surfaces, which causes them to repel each other—much like tiny magnetic bumper cars gliding past one another. This repulsion allows blood cells to circulate smoothly, delivering oxygen and nutrients efficiently throughout the body.
Red light therapy helps blood flow more freely throughout the body, improving circulation so that oxygen and essential nutrients reach tissues more efficiently. By reducing blood viscosity and supporting vessel relaxation, it also lowers the risk of stagnation or blockages, helping the cardiovascular system function more smoothly and effectively. When the electrical charge of blood cells is maintained and supported, circulation remains optimal, ensuring tissues are nourished and the risk of clumping or sluggish blood flow is minimized.
2. Boosts Celluar Energy (ATP)
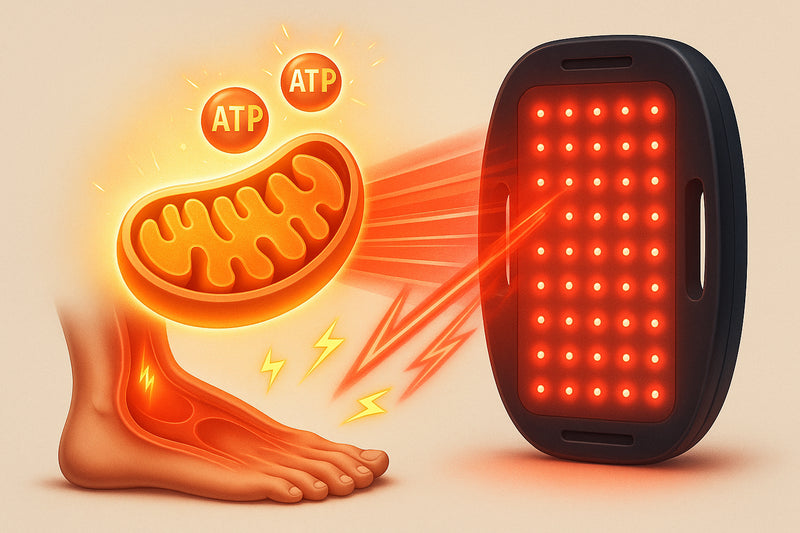

The body transforms radiant light energy into biological energy through two main mechanisms:
- Mitochondrial ATP Production – Think of your mitochondria as tiny solar panels inside your cells. When they absorb red and near-infrared (NIR) light, they generate ATP—the cellular “fuel”—more efficiently, powering every function in your body.
- Intracellular Water Photoelectric Effect – The water inside your cells also plays a role. When exposed to light, this structured water can store and release electrical energy, enhancing cellular communication and function.
3. Reduce Inflammation
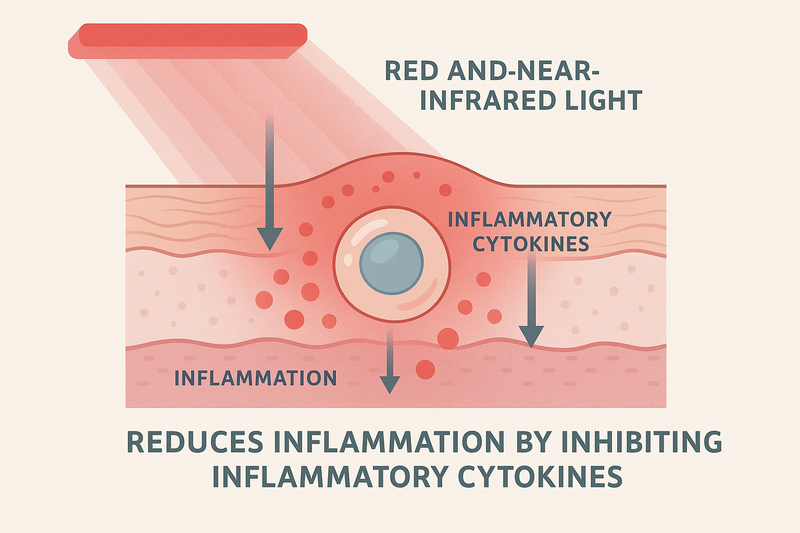
Red light therapy stimulates cellular energy, improves circulation, and balances immune signaling, which together lower inflammatory cytokines and speed healing.
Conditions Supported by Red Light Therapy
Why It’s Gaining Popularity
Red light therapy stands out because it is non-invasive, drug-free, and has minimal side effects. Unlike many treatments, it doesn’t require recovery time or carry risks of skin damage. Devices are now widely available for at-home use, making it more accessible than ever.













